1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane (CAS 6940-78-9): Key Chemical Facts
Introduction to 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane (CAS 6940-78-9)
1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane, identified by the CAS number 6940-78-9, is a significant chemical compound primarily utilized as an intermediate in various organic synthesis processes. While not a medication you would directly consume, its role in the background is crucial for the development of certain pharmaceutical drugs and other specialty chemicals. This article provides an overview of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane (CAS 6940-78-9), detailing its properties, applications, safety considerations, and how it’s made. Understanding such chemical building blocks is essential for appreciating the complexity and innovation within the pharmaceutical industry.
Chemical Properties of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane
1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane is a liquid organic compound with distinct physical and chemical characteristics that make it valuable for specific chemical reactions.
- Appearance: It is typically a colorless to pale yellow or light brown liquid.
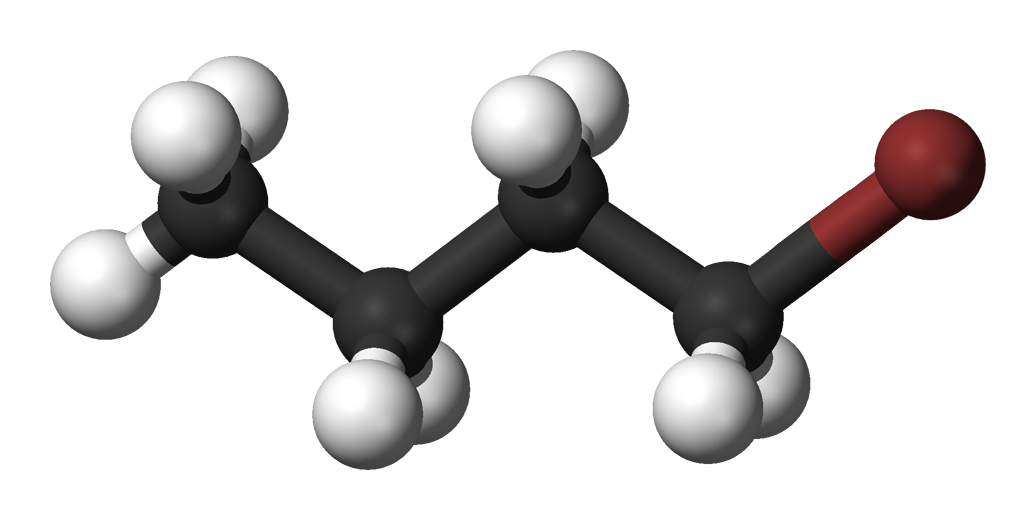
- Molecular Formula: Its chemical formula is C4H8BrCl. This indicates it has a four-carbon chain with one bromine atom and one chlorine atom attached.
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 171.46 g/mol.
- Boiling Point: It has a boiling point typically in the range of 175-177 °C (347-351 °F).
- Solubility: 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane is generally poorly soluble in water but dissolves well in common organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and acetone. This solubility profile is important for its use in various reaction conditions.
- Stability: It is a relatively stable compound under standard storage conditions but, like many haloalkanes, it can be reactive. It should be stored away from strong oxidizing agents and bases. Its bifunctional nature, having both bromo and chloro groups, allows for selective reactivity in chemical synthesis. The presence of two different halogens (bromine and chlorine) on the same molecule offers chemists flexibility in designing synthetic pathways, as bromine is generally more reactive than chlorine in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Uses & Applications of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane (CAS 6940-78-9)
The primary significance of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane (CAS 6940-78-9) lies in its role as a versatile intermediate chemical and building block in organic synthesis. It is not typically used as an end-product itself but is crucial in constructing more complex molecules.
- Pharmaceutical Synthesis: One of the most important pharmaceutical uses of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane is as a precursor or intermediate in the synthesis of various Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). It provides a four-carbon chain that can be incorporated into larger drug molecules. For instance, it has been reported as an intermediate in the synthesis of drugs like buspirone, an anti-anxiety medication, and other compounds used in creating therapeutic agents. Its ability to participate in reactions forming carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bonds is key to its utility.
- Organic Synthesis: Beyond pharmaceuticals, it serves as a valuable reagent in general organic chemistry. It can be used to introduce a 4-chlorobutyl group or, through further reactions, a 4-bromobutyl group into target molecules. This makes it useful for creating various aliphatic and heterocyclic compounds.
- Agrochemicals: Similar to its role in pharmaceuticals, it can also be an intermediate in the production of certain agrochemicals, although this is a less commonly highlighted application.
- Research and Development: In chemical research laboratories, 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane is employed in exploring new synthetic routes and developing novel compounds with potential therapeutic applications or other industrial uses.
Benefits of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane in Pharmaceuticals
The benefits of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane in the pharmaceutical sector are indirect but substantial, stemming from its utility as a specialized chemical intermediate.
- Versatile Building Block: Its structure, featuring both a bromine and a chlorine atom, provides chemists with flexibility. Bromine is typically more reactive and can be targeted first in a reaction sequence, leaving the chlorine atom for subsequent modification. This differential reactivity is a significant advantage in multi-step syntheses.
- Enabling Complex Molecule Synthesis: 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane allows for the introduction of a defined four-carbon linear chain, which is a common structural motif in many biologically active molecules. This facilitates the construction of complex drug candidates that might otherwise be difficult to synthesize.
- Cost-Effectiveness in Specific Routes: For certain synthetic pathways, using 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane can be a cost-effective way to achieve the desired molecular structure compared to alternative starting materials or more convoluted routes.
- Contribution to Therapeutic Innovations: By enabling the synthesis of novel or existing pharmaceutical compounds, it indirectly contributes to the development of treatments for various diseases. Many life-saving and life-enhancing medications rely on such specific chemical intermediates for their production. The molecular stability of the compound under specific reaction conditions, while allowing for targeted reactivity, is a key benefit.
Safety Profile: Hazards & Precautions for 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane
As 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane (CAS 6940-78-9) is an industrial chemical and not a drug for direct patient use, its safety profile relates to occupational exposure and handling. It is important to consult Safety Data Sheets (SDS) provided by suppliers for comprehensive information.
- Potential Hazards:
- Skin Irritation: Can cause skin irritation upon contact. Prolonged or repeated exposure may lead to dermatitis.
- Eye Irritation: Likely to cause serious eye irritation.
- Respiratory Irritation: Vapors or mists may irritate the respiratory tract.
- Harmful if Swallowed or Inhaled: Ingestion or inhalation of significant amounts can be harmful.
- Combustible: It is a combustible liquid and should be kept away from heat, sparks, and open flames.
- Precautions and Safety Guidelines:
- Handling: Use only in well-ventilated areas or with appropriate respiratory protection. Wear protective gloves, safety goggles or a face shield, and chemical-resistant clothing to prevent skin and eye contact.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated place in tightly sealed containers. Keep away from incompatible materials such as strong oxidizing agents and strong bases.
- First Aid: In case of skin contact, wash immediately with plenty of water and soap. If in eyes, rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. If inhaled, move person to fresh air. If swallowed, seek medical attention immediately.
- Disposal: Dispose of waste and residues in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations. This chemical should not be released into the environment.
Regulatory bodies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US and equivalent agencies in other regions provide guidelines for handling such chemicals in workplace settings to ensure safety.
Manufacturing Process of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane
The synthesis of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane typically involves multi-step chemical reactions. While the exact proprietary methods can vary between manufacturers, a general understanding can be described for a layperson.
One common approach involves starting with a readily available precursor like tetrahydrofuran (THF) or 1,4-butanediol.
If starting with THF (a cyclic ether), the ring structure can be opened using hydrogen bromide (HBr) to form 4-bromobutanol. This intermediate alcohol can then be reacted with a chlorinating agent (like thionyl chloride, SOCl2) to replace the hydroxyl (-OH) group with a chlorine atom, yielding 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane.
Alternatively, starting from 1,4-butanediol (a di-alcohol), one hydroxyl group can be selectively replaced by bromine and the other by chlorine using specific brominating and chlorinating agents in a controlled sequence.
The entire manufacturing process of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane requires careful control of reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and stoichiometry (the specific amounts of reactants) to ensure high purity and yield of the final product. Purification steps, such as distillation, are typically employed to isolate 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane of the desired quality for its applications, especially in pharmaceutical uses.
FAQ Section
- Q1: Is 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane (CAS 6940-78-9) safe to handle at home?
No, 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane is an industrial chemical intended for use by trained personnel in controlled laboratory or manufacturing settings. It is not a consumer product and can be hazardous if handled improperly. Always follow an official Safety Data Sheet (SDS).
- Q2: What is 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane primarily used for in pharmaceuticals?
Its primary role in pharmaceuticals is as an intermediate or a building block. This means it is a key ingredient used in the chemical synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). It’s not a drug itself but helps create them.
- Q3: Why does 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane have both bromine and chlorine?
Having both bromine and chlorine atoms gives chemists more options during synthesis. Bromine is generally more reactive than chlorine in many common reactions. This difference in reactivity (known as differential reactivity) allows for selective chemical transformations, making it a versatile tool in creating complex molecules for therapeutic applications.
- Q4: Is 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane a common chemical?
While not a household name, 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane (CAS 6940-78-9) is a known and utilized compound within the chemical and pharmaceutical industries for specific synthetic purposes due to its unique structure. Its availability is important for researchers and manufacturers involved in organic synthesis.
- Q5: Are there alternatives to using 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane in synthesis?
Yes, chemists often have multiple pathways to synthesize a target molecule. There can be other reagents or building blocks that serve a similar purpose to 1-Bromo-4-chlorobutane. The choice often depends on factors like the desired yield, cost, safety, availability of starting materials, and the specific reaction steps involved in the overall synthesis.
- +86 13345119692
- +86 15550440621
- pharm@sinocurechem.com