Introduction
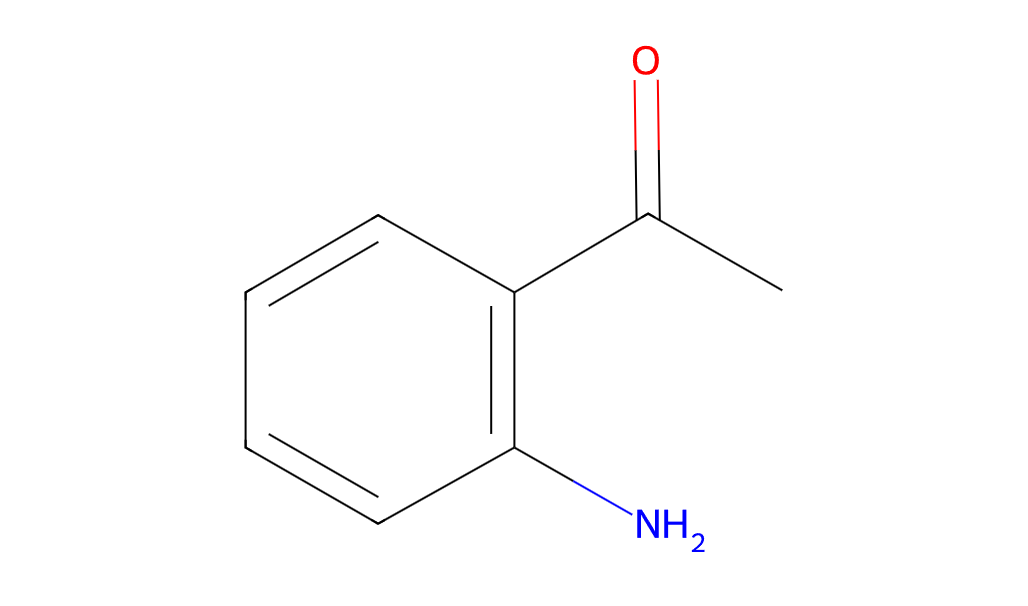
2-Aminoacetophenone, with the chemical formula C8H9NO and CAS number 551-93-9, is an organic compound widely recognized in various industries, particularly pharmaceuticals. This yellow to yellow-brown liquid, notable for its distinctive grape-like odor, serves as a crucial intermediate in organic synthesis and has unique applications stemming from its chemical properties. In this article, we’ll dive into the chemical properties, uses, benefits, potential side effects, and manufacturing process of 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9), offering a clear and comprehensive guide for readers seeking to understand this versatile compound.
Chemical Properties of 2-Aminoacetophenone
2-Aminoacetophenone features a molecular structure comprising a benzene ring substituted with an amino group (-NH2) and an acetyl group (-COCH3). The amino group is positioned ortho (adjacent) to the acetyl group, influencing its reactivity and chemical behavior. Below are its key chemical and physical properties:
- Molecular Weight: 135.16 g/mol
- Melting Point: Approximately 20°C
- Boiling Point: 251.8°C at 760 mmHg
- Density: 1.096 g/cm³
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water; highly soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, methanol, and acetone
- Appearance: Yellow to yellow-brown liquid
- Odor: Grape-like
These characteristics make 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) well-suited for a range of chemical reactions, especially in synthesizing complex molecules used in pharmaceuticals and other industries.
Uses and Applications of 2-Aminoacetophenone
2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) is valued for its versatility across multiple fields, with its primary role as an intermediate in organic synthesis standing out. Here are some of its key uses:
- Pharmaceutical Intermediates: It acts as a building block in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds, including potential analgesics and anti-inflammatory agents.
- Organic Synthesis: Beyond pharmaceuticals, it contributes to producing dyes, fragrances, and other organic chemicals.
- Flavoring Agent: Its grape-like scent makes it a volatile flavor component in certain food products, such as masa corn flour items.
- Diagnostic Marker: The compound’s association with Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth allows it to serve as a diagnostic tool in medical settings, notably for detecting infections in burn wounds.
These diverse applications underscore the importance of 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) in both industrial and scientific contexts.
Benefits of 2-Aminoacetophenone
The use of 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) provides several notable advantages:
- Versatility in Synthesis: Its molecular structure supports a broad array of chemical reactions, making it an essential intermediate for creating diverse compounds.
- Efficiency in Production: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, it can streamline synthesis processes, potentially reducing production time and costs.
- Diagnostic Utility: Its link to Pseudomonas aeruginosa offers a non-invasive method for identifying infections, aiding medical diagnostics.
- Flavor Contribution: In food applications, its grape-like aroma enhances the sensory qualities of certain products.
These benefits highlight why 2-Aminoacetophenone remains a compound of interest across various sectors.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions for 2-Aminoacetophenone
While 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) is highly useful, it requires careful handling due to potential risks. Below are some key considerations:
- Toxicity: It may be harmful if ingested or if it contacts skin or eyes. Protective gear like gloves and goggles is recommended during handling.
- Irritation: Inhalation can irritate the respiratory system, necessitating proper ventilation in workspaces.
- Flammability: As an organic compound, it is combustible and should be stored away from flames or ignition sources.
- Environmental Concerns: Disposal must follow local regulations to avoid environmental harm.
Adhering to these precautions ensures the safe use of 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) in industrial and laboratory settings.
Manufacturing Process of 2-Aminoacetophenone
The production of 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) typically involves reducing 2-nitroacetophenone, with two common methods employed:
- Iron Powder Reduction: 2-Nitroacetophenone is reacted with iron powder and hydrochloric acid under controlled temperatures to convert the nitro group (-NO2) to an amino group (-NH2).
- Catalytic Hydrogenation: Alternatively, a catalyst like palladium on carbon is used with hydrogen gas, offering an efficient and cleaner reaction process.
Post-reduction, the crude product undergoes purification via distillation under reduced pressure or recrystallization in suitable solvents. This step ensures the high purity required for pharmaceutical applications. Quality control, including spectroscopic techniques like NMR and IR, verifies the final product’s identity and purity. This manufacturing process reflects the precision and care needed to produce 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) for industrial use.
Conclusion
2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) stands out as a multifaceted compound with significant roles in pharmaceuticals, organic synthesis, food flavoring, and medical diagnostics. Its chemical properties—such as its solubility and molecular structure—enable its use as a vital intermediate in diverse chemical processes. The compound offers benefits like versatility and efficiency, yet demands careful handling due to potential toxicity and flammability risks. Its manufacturing process, reliant on precise reduction and purification techniques, underscores the quality standards required for its applications. As industries evolve, 2-Aminoacetophenone (CAS 551-93-9) continues to be a valuable asset for scientific and industrial advancements.