Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0): A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Trifluoromethanesulfonyl chloride, often referred to as triflyl chloride, is a specialized chemical compound identified by the CAS number 421-83-0. While not a household name, this organosulfur compound plays a critical role as a reagent and intermediate in various complex chemical syntheses, particularly within the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries. This article provides a detailed look at Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0), covering its chemical properties, common applications, associated benefits, necessary safety precautions, and an overview of its manufacturing process. Understanding this compound is key for professionals involved in advanced organic synthesis and drug discovery.
Chemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0)
Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) possesses distinct chemical and physical properties that define its utility and handling requirements.
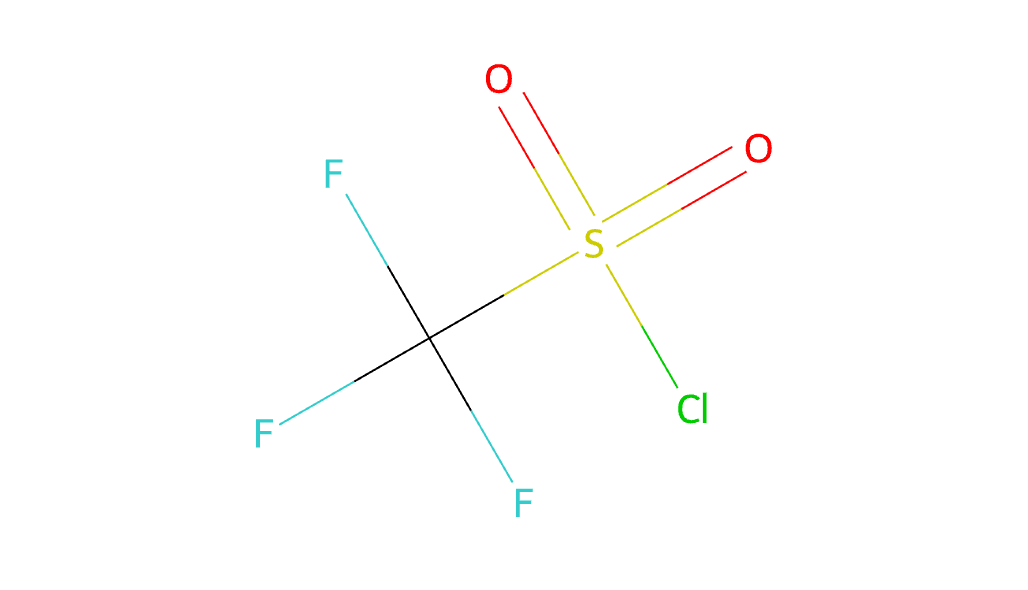
- Chemical Formula: Its molecular formula is CF3SO2Cl.
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 168.52 g/mol.
- Appearance: Under standard conditions, it is typically encountered as a colorless gas or a fuming liquid, depending on temperature and pressure. It often has a sharp, pungent odor.
- Reactivity: Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride is known for its high reactivity, particularly towards nucleophiles (electron-rich species). Its most significant reaction involves the introduction of the trifluoromethanesulfonate group (CF3SO2-), commonly known as the triflyl group. This group is an exceptionally good leaving group in organic reactions, meaning it detaches readily from a molecule, facilitating subsequent chemical transformations.
- Sensitivity: The compound is highly sensitive to moisture. It reacts vigorously, sometimes violently, with water and protic solvents (like alcohols) to release corrosive hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas and trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (triflic acid), which is itself a superacid. This necessitates handling under anhydrous (water-free) conditions.
- Solubility: It is generally soluble in anhydrous aprotic organic solvents such as dichloromethane, diethyl ether, and tetrahydrofuran (THF).
- Stability: While highly reactive, Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) is relatively stable when stored properly under inert, anhydrous conditions, typically refrigerated.
Understanding these properties is crucial for the safe and effective use of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride in any application.
Uses and Applications of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0)
The primary value of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) lies in its ability to introduce the triflyl group (CF3SO2-) onto other molecules. This function makes it a vital reagent in several fields:
-
Organic Synthesis: This is the most prominent area of application. Triflyl chloride is widely used to convert alcohols into triflates (trifluoromethanesulfonates). Alcohols generally have poor leaving groups (-OH), but converting them to triflates (-OTf) transforms them into excellent leaving groups. This activation facilitates important reactions like nucleophilic substitutions (SN1 and SN2) and elimination reactions (E1 and E2), which are fundamental steps in building complex organic molecules. Phenols can similarly be converted to aryl triflates, which are valuable substrates for cross-coupling reactions (e.g., Suzuki, Stille couplings) used extensively in drug discovery.
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediate: Due to its role in facilitating key synthetic steps, Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) serves as a critical intermediate or reagent in the synthesis pathways of numerous active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its ability to activate alcohols or phenols enables chemists to construct the complex molecular architectures often required for biologically active compounds, including certain anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-cancer agents, and antivirals. The efficiency provided by the triflate leaving group is often essential for achieving viable yields in multi-step syntheses.
-
Agrochemical Synthesis: Similar to pharmaceuticals, the agrochemical industry utilizes Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride for synthesizing complex molecules used in pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides. The triflate group facilitates reactions needed to build the specific structures required for agricultural activity.
-
Chemical Research: In academic and industrial research laboratories, Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) is a standard reagent for exploring new synthetic methodologies and preparing novel compounds. Its well-understood reactivity and the reliable performance of the triflate leaving group make it a go-to tool for synthetic chemists.
-
Material Science: While less common, derivatives prepared using triflyl chloride may find applications in creating specialized polymers or materials with unique electronic or physical properties.
The versatility of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) in creating reactive intermediates makes it indispensable in fields requiring advanced chemical synthesis.
Benefits of Using Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride
The use of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) offers significant advantages in chemical synthesis:
- Creation of Excellent Leaving Groups: As mentioned, the triflate group (-OTf) is one of the best known leaving groups in organic chemistry. This dramatically increases the rate and efficiency of subsequent substitution or elimination reactions compared to using less reactive precursors like alcohols directly.
- Increased Reaction Efficiency: By enabling reactions under milder conditions or reducing reaction times, triflyl chloride can improve overall process efficiency and yield, which is particularly important in costly pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Versatility: It can be used to activate a wide range of alcohols (primary, secondary, tertiary) and phenols, making it applicable to diverse synthetic challenges.
- Facilitation of Complex Syntheses: The reliable activation provided by Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride allows chemists to perform transformations that might otherwise be difficult or impossible, enabling the construction of highly complex target molecules.
- Well-Established Chemistry: The reactions involving triflyl chloride are well-documented and understood, providing a degree of predictability for synthetic chemists.
These benefits underscore why Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) remains a key reagent despite its handling challenges.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions for Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0)
Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) is a hazardous substance and must be handled with extreme caution by trained personnel only. It is crucial to understand that this compound is not a drug for direct administration and the “side effects” relate to exposure during handling.
- Corrosivity: It is highly corrosive to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Contact can cause severe chemical burns.
- Respiratory Irritation: Inhalation of the gas or fumes can cause severe irritation or burns to the respiratory tract, potentially leading to pulmonary edema.
- Reaction with Water: Its violent reaction with water produces highly corrosive substances (HCl and triflic acid), increasing the hazard potential in humid environments or during spills.
- Toxicity: While specific long-term toxicity data might be limited, acute exposure is clearly dangerous due to its corrosive nature.
Handling Precautions:
- Engineering Controls: Always handle Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) in a certified chemical fume hood with good ventilation to prevent inhalation exposure.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Mandatory PPE includes chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., butyl rubber, Viton), chemical splash goggles, a face shield, and a chemically resistant lab coat or apron. Respiratory protection may be needed depending on the scale and procedure.
- Anhydrous Conditions: Use only dry glassware and equipment. Perform reactions under an inert atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or argon) to prevent contact with atmospheric moisture.
- Storage: Store in a tightly sealed container, often under inert gas, in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from water, bases, oxidizing agents, and other incompatible materials. Refrigeration is common.
- Spill Management: Have appropriate spill kits ready (containing non-aqueous absorbents). Neutralization procedures should avoid water if possible or use extreme caution.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Always consult the manufacturer’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) before handling. It contains detailed information on hazards, first aid, and emergency procedures.
Strict adherence to safety protocols is non-negotiable when working with this compound.
Manufacturing Process of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride
The industrial synthesis of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) typically involves complex chemical processes carried out under carefully controlled conditions, often requiring specialized equipment due to the corrosive and reactive nature of the intermediates and product.
While specific proprietary methods vary, common approaches often start from precursors like trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (CF3SO3H) or its anhydride ($ (CF_3SO_2)_2O $). A key step usually involves chlorination using reagents like thionyl chloride (SOCl2), phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5), or other chlorinating agents capable of converting a sulfonic acid or related group into the sulfonyl chloride ($ -SO_2Cl $) functionality.
For example, a possible route involves reacting trifluoromethanesulfonic acid with a chlorinating agent under specific temperature and pressure conditions.
$ CF_3SO_3H + PCl_5 \rightarrow CF_3SO_2Cl + POCl_3 + HCl $ (Simplified representation)
The reaction must be conducted under strictly anhydrous conditions. Following the reaction, purification steps such as distillation are essential to isolate Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) at the high purity level required for its applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical industry where impurity control is paramount. Quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure the final product meets stringent specifications.
Conclusion
Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0), or triflyl chloride, is a powerful and versatile reagent essential for modern organic synthesis. Its ability to form the highly effective triflate leaving group makes it invaluable in constructing complex molecules, particularly within pharmaceutical and agrochemical development. While its benefits in facilitating challenging chemical transformations are significant, its hazardous nature demands rigorous safety protocols and handling by experienced professionals. The controlled manufacturing process ensures the availability of high-purity Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride (CAS 421-83-0) needed for these critical applications, solidifying its place as a key tool in the chemist’s arsenal.