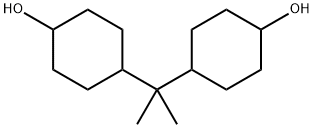
Product Description:
Hydrogenated bisphenol A (HBPA), also known as 4,4′-(Propane-2,2-diyl)dicyclohexanol, is the hydrogenated derivative of bisphenol A. It typically appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder or flakes. HBPA is valued for its enhanced thermal stability, improved weatherability, and superior UV resistance compared to conventional bisphenol A. These properties make it a crucial intermediate in the production of high-performance polymers, particularly epoxy resins, polyester resins, and specialized coatings, where durability and color stability are paramount.
Product Properties:
Property Value Chemical Name
Hydrogenated bisphenol A; 4,4′-(Propane-2,2-diyl)dicyclohexanol
CAS Number
80-04-6
Molecular Formula
C₁₅H₂₈O₂
Molecular Weight
240.39 g/mol
Appearance
White to off-white crystalline powder or flakes
Melting Point
Approximately 185-195 °C (can vary with isomeric purity)
Boiling Point
High, typically decomposes before boiling at atmospheric pressure
Solubility
Soluble in many organic solvents (e.g., acetone, methanol, ethyl acetate); sparingly soluble in water
Synonyms
HBPA; Dicyclohexanolpropane; 4,4′-Isopropylidenedicyclohexanol; 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)propane
Product Usage:
Epoxy Resins: Used as a curative or building block to produce epoxy resins with excellent clarity, low color, superior UV stability, and improved weather resistance, suitable for outdoor applications and protective coatings. For example, in clear coats for automotive or marine applications.
Unsaturated Polyester Resins (UPR): Incorporated into UPR formulations to enhance their chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical properties, often used in manufacturing high-performance composites and gel coats.
Saturated Polyester Resins: Utilized in the synthesis of saturated polyester resins for powder coatings, coil coatings, and can coatings, providing good flexibility, adhesion, and resistance to yellowing.
Polycarbonates: Can be used to produce specialized polycarbonates with improved optical properties and resistance to weathering.
Adhesives and Sealants: Employed in formulations for high-performance adhesives and sealants requiring good environmental resistance.
Polyurethanes: Acts as a polyol in the production of polyurethanes, contributing to enhanced durability and stability.
Electrical Laminates: Used in the manufacture of electrical laminates for printed circuit boards (PCBs) where high thermal stability and good dielectric properties are needed.
Contact Us Now!
If you need MSDS,TDS or sample testing, please email us at pharm@sinocurechem.com or use the website live chat to get prompt reply.
- +86 13345119692
- +86 15550440621
- pharm@sinocurechem.com